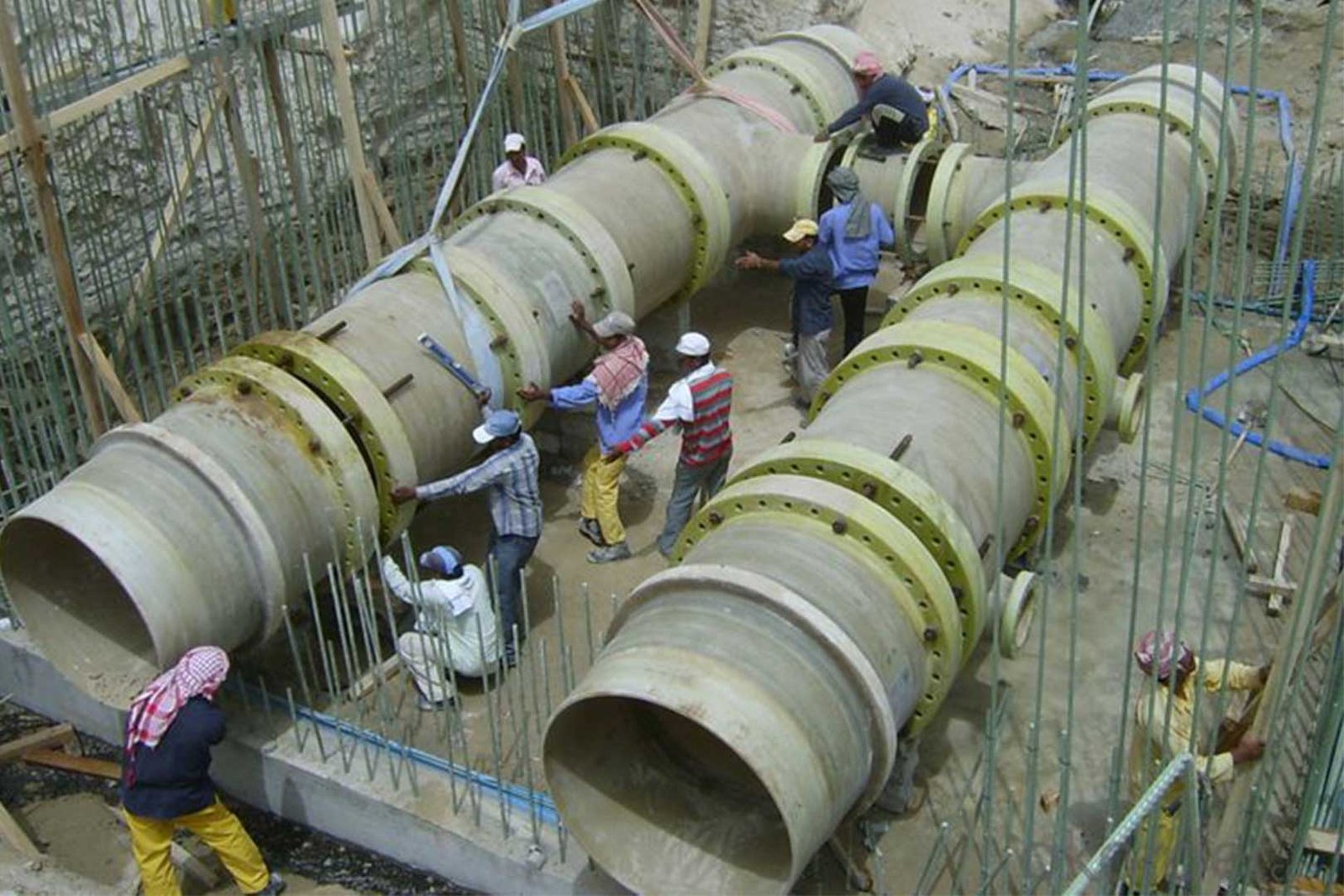
Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP) pipes have revolutionized piping solutions globally due to their lightweight nature, durability, and resistance to aggressive environments. GRP pipes, a magnificent combination of glass fiber in a resin matrix, are expected to reach a global market value of $7.5 billion by 2028. Therefore, understanding the pros and cons of GRP pipes enables engineers, project managers, and contractors to select the best pipeline.
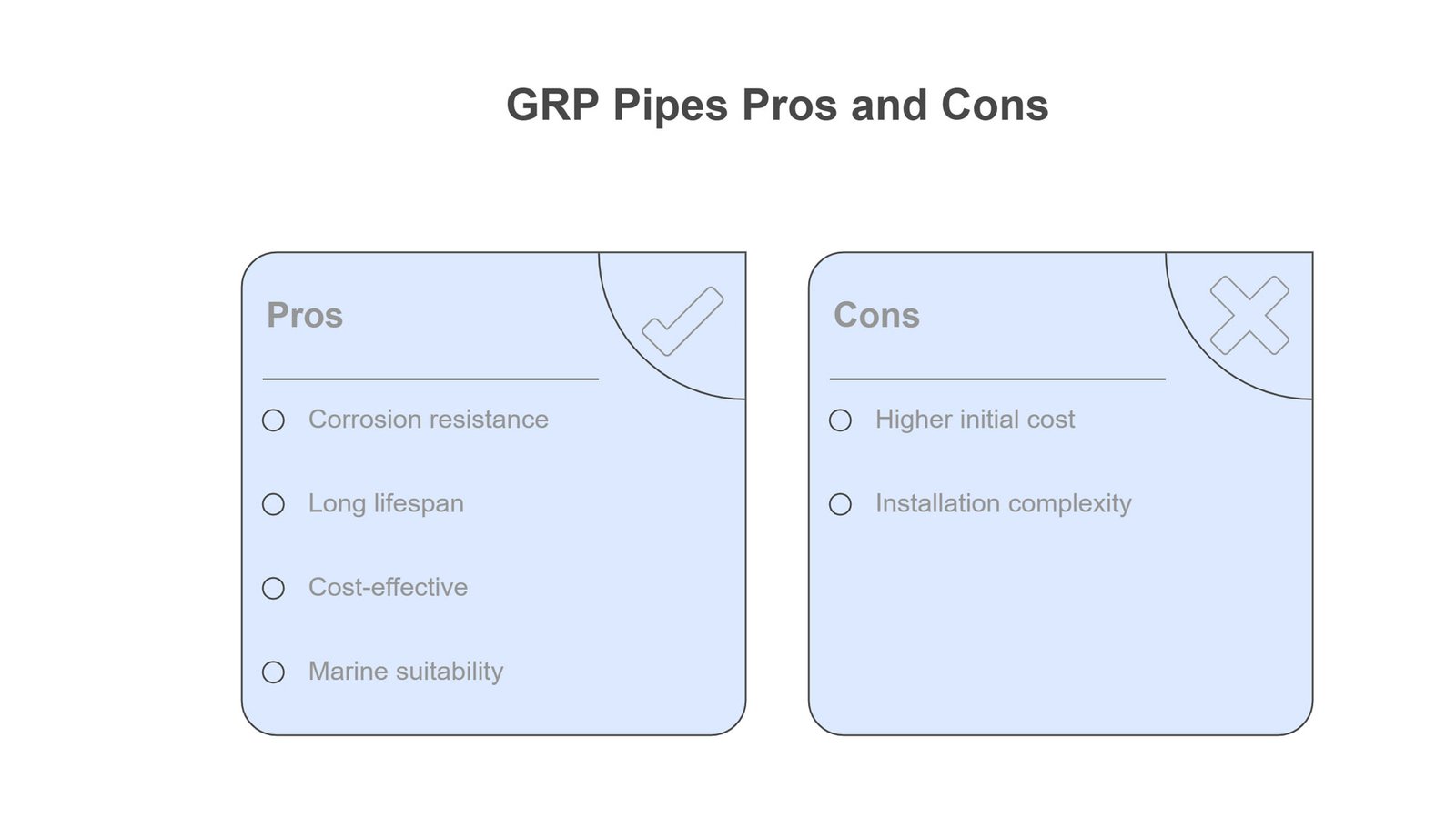
GRP pipes offer various benefits, such as resistance against corrosion and a long lifespan. Their lightweight and smooth inner surface saves costs and lowers the need for maintenance. However, they’re brittle, require careful transportation and specialized repairs with trained workers, have a -40°C to 100°C temperature tolerance range, present issues with large-scale usage, and limited diameters.
In this article, we’ll evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of GRP pipes to meet the demands of your special projects.
8 Key Advantages of GRP Pipes: Why They’re a Top Choice for Modern Projects
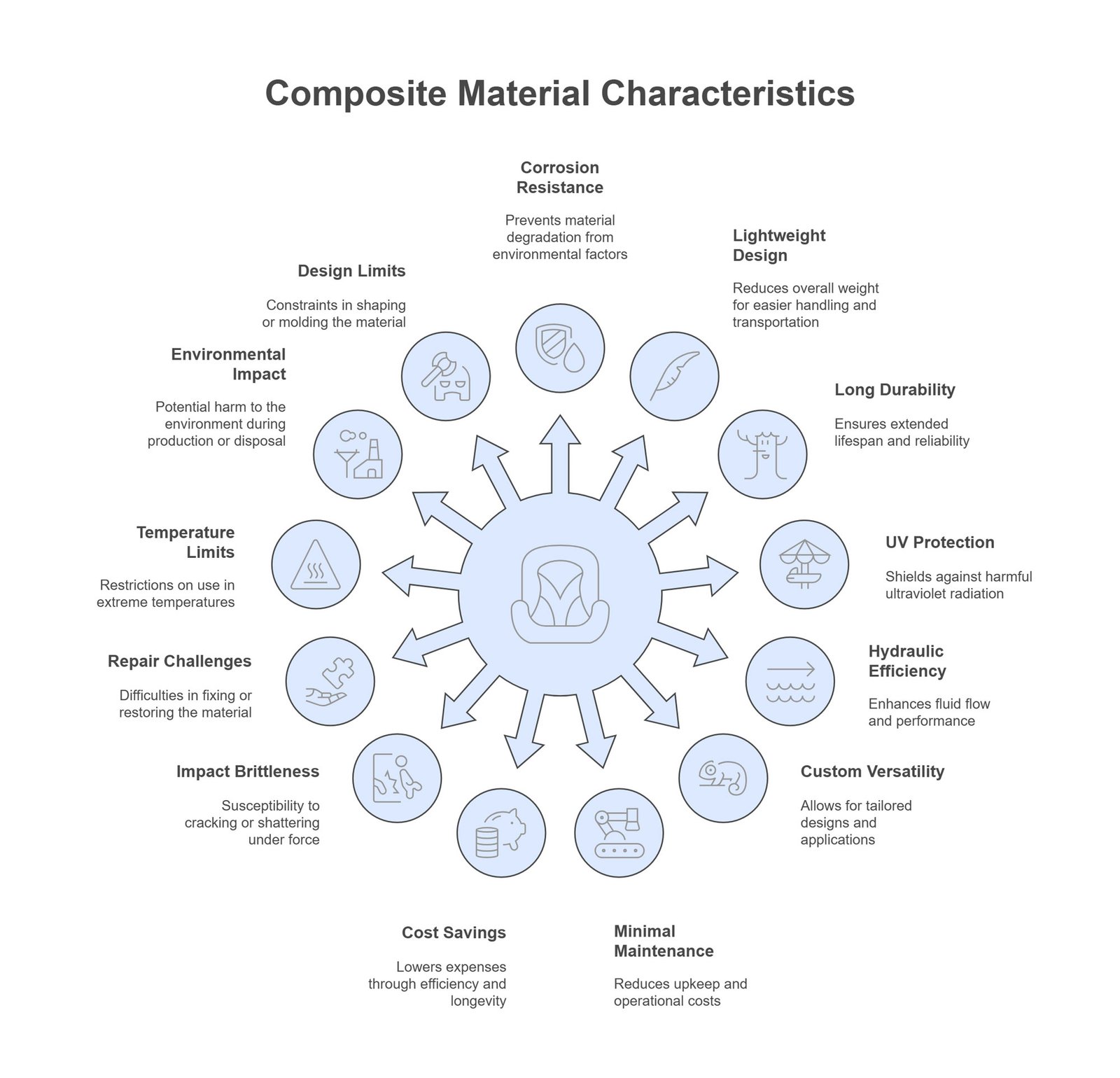
GRP pipes provide a wide range of benefits like corrosion resistance, lightweight design, and long lifespan, making them perfect for water, wastewater, and marine projects. Unlike steel pipes, these advantages can save costs and the need for maintenance.
1. Corrosion Resistance
GRP pipes excel in harsh environments due to their resistance to corrosion from chemicals, acids, alkalis, and saline conditions, which traditional materials like steel or concrete often fail to withstand. For instance, in desalination plants, GRP pipes exhibit no degradation over decades in seawater, whereas steel pipes are more prone to corrosion under the same conditions.
According to ScienceDirect, the GRP pipe’s corrosion resistance enables long-term service in industrial applications such as chemical transmission or wastewater treatment while decreasing the cost of replacement.
In Middle Eastern desalination projects, GRP pipe represents itself as a strong pipeline that lasts over 50 years, unlike metal alternatives, making it the top choice for marine and industrial uses.
2. Lightweight & Easy Handling
Lightweight and easy handling of GRP pipes are two other benefits that make GRP pipes superior to old-fashioned materials like steel or concrete.
GRP pipes weigh about one-fourth of steel pipes and 10% of concrete, which results in cost and time savings in both installation and transportation. For instance, unlike steel pipes, GRP pipes don’t need to be transported by heavy machinery like cranes, while a longer section of GRP pipes reduces the cost of jointing and saves time.
Also, in difficult-to-access projects like offshore platforms, the lightweight nature of GRP pipes can decrease almost 50% of labor costs compared to steel pipes.
3. Durability & Long Service Life
GRP pipes remain for decades with no degradation or corrosion in harsh conditions and, surprisingly, can resist for almost 100 years under proper conditions. In wastewater systems and chemical pipelines, the high resistance from corrosion and physical damage recreate such a performance that steel or concrete fails.
Also, steel or concrete cracks under seismic zones at least require regular maintenance, which GRP pipes avoid. For example, GRP pipes minimize the cost of maintenance over decades in infrastructure projects.
4. UV & Weather Resistance
GRP pipes resist degradation from sunlight exposure due to built-in UV equipment that makes them perfect for above-ground pipelines like irrigation. They also provide structural integrity across diverse climates, from scorching deserts to freezing conditions, avoiding cracks or other failures.
Unlike metal pipes that may corrode or PVC pipes that may be damaged under UV exposure, GRP pipe UV resistance shows a long-term performance in outdoor applications and aboveground installations.
5. Hydraulic Efficiency
GRP pipes contain such a smooth internal surface that can decrease the cost of energy for pumping, while ResearchGate highlights a roughness coefficient of 0.0084 (compared to 0.013 for cast iron) reduces friction loss.
Therefore, in water distribution or sewage systems where fluid transport is continuous, compared to steel pipe, GRP pipe improves the water flow rates and system performance and lowers head loss and the pumping energy needed by up to 20%.
6. Customization & Versatility
GRP pipes, with extensive customized options, allow manufacturers to design their desired pipeline through characteristics like pipe thickness, diameter, and pressure ratings to meet specific project requirements.
Moreover, GRP pipes can adapt to various conditions and make them flawless for buried, aboveground, or marine installations; engineers can change the resin base to create chemical resistance or structural strength in applications like potable water lines, industrial piping, or marine GRP pipe solutions.
For example, GRP pipes can be designed for high-pressure water systems or low-pressure irrigation plants while keeping flexibility compared to alternatives like concrete.
7. Economic Advantages
While primary costs for GRP pipes may be higher than PVC, their lifecycle cost analysis apparently shows 20–40% savings compared to steel due to lower installation, maintenance, and replacement costs.
Their low residual value also reduces the risk of theft, a significant issue with metal pipes in some regions. For procurement managers, this makes GRP pipes a cost-effective investment for long-term projects like water supply or industrial systems.
| Cost Factor | GRP Pipes | Steel Pipes | Concrete Pipes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Moderate | High | High |
| Installation | Low | High | Very High |
| Maintenance | Low | High | Moderate |
| Lifecycle Cost | Low | High | Moderate |
8. Low Maintenance & Safety
Selecting GRP pipes for your project can reduce the need for maintenance and installation costs due to their corrosion-resistant properties. Unlike steel pipes, which need regular maintenance, GRP pipes barely require repairs or replacements.
Additionally, as a choice in the manufacturing process of GRP pipe, anti-slip GRP pipe surfaces increase safety in wet or industrial environments, such as platforms or walkways, where metal pipes may fail due to slip hazards.
| Advantage | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Resists chemicals, acids, alkalis, and marine environments | Extends lifespan, reduces replacements in harsh conditions |
| Lightweight & Easy Handling | 35% of steel, 10% of concrete weight | Lowers transport and installation costs, ideal for remote sites |
| Durability & Long Service Life | 50–100+ year lifespan, resists abrasion | Minimizes maintenance, ensures long-term reliability |
| UV & Weather Resistance | UV inhibitors ensure outdoor durability | Maintains integrity in diverse climates |
| Hydraulic Efficiency | Smooth surface reduces friction loss | Saves 10–20% on pumping energy costs |
| Customization & Versatility | Tailored thickness, diameter, pressure ratings | Suits buried, above-ground, and marine applications |
| Low Maintenance & Safety | Minimal upkeep, anti-slip surfaces available | Reduces costs, enhances safety in wet environments |
| Economic Advantages | Lower lifecycle costs, reduced theft risk | Saves 20–40% over steel, improves ROI |
Common Disadvantages and Limitations of GRP Pipes
GRP pipe includes infinite benefits, such as corrosion resistance or lightweight design, as we mentioned above. However, there are some limitations, from impact brittleness to recycling challenges, that require to be planned carefully:
1. Impact Brittleness
GRP pipes, due to their composite structure, are vulnerable to cracks if mishandled during transportation or installation. Mishandling can be dropping or striking the pipes. To avoid GRP pipe impact brittleness, contractors must use padded supports and avoid stacking pipes during the storage process.
Practices such as pipes’ transportation via lifting slings in cradles to prevent further happenings. For example, guidelines from manufacturers suggest storing GRP pipes on flat, padded surfaces to decrease stress points.
Also, workers should be trained to handle the pipes and transport them carefully to reduce damage risks, especially on large-scale projects where several pipe sections are about to move and be stored.
2. Repair Challenges
There are two main techniques and materials, such as resin patching or fiberglass wrapping in GRP pipe repairing, which involves some challenges.
Unlike steel pipes, which can be welded, GRP repairs often require trained professionals to cut out the damaged part and replace it with a new segment through adhesive bondage or mechanical couplings. This process can cost 2–3 times more than metal pipe repairs, though metal pipes are more likely to need repairing due to their lower corrosion resistance.
Overall, Professional handling and training are critically required to provide such reliable maintenance and repair. Contractors should budget for these costs while increasing the access to skilled technicians to lower any project delays.
3. Temperature Limitations
GRP pipes are able to handle a temperature range of -40°Cto100°C, which is unfortunately not counted as a good choice for applications involving extreme heat without modifications. (Source: EuroPlas)
Due to the GRP pipe temperature limitations, standard resins may lose their shape above 100°C. High-temperature applications, such as hot oil or steam pipelines, require special heat-resistant resins, which can increase material costs by 20–30%.
Engineers must consider temperature requirements during the design phase to select appropriate resin types (e.g., epoxy, polyester, or vinylester). For example, vinyl ester resins can manage the temperature range changing, but costs and availability must be considered.

4. Environmental & Recycling Concerns
The production of GRP pipes involves resin-based chemicals that can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), raising GRP pipe environmental impact concerns. (Source: BHEL)
Moreover, the GRP pipes recycling process is challenging due to their composite base (the separation of glass fibers from resin is a complex and expensive process, which probably isn’t worth it).
Mechanical grinding is a new recycling method for GRP pipes, while most GRP waste ends up in landfills. Then, engineers seeking eco-friendly pipelines should consider this point and select the best option that matches their demands.
5. Manufacturing Size and Design Limits
The manufacturing size and design limits of GRP pipe can create some dilemmas in transportation and pipe’s performance. As huge diameters (around 4 meters) and high-rated wall thickness can increase cost or lower the flexibility. Also, these limitations can make GRP pipes less appropriate for large-scale projects like water, wastewater, and high-pressure systems that need larger sizes or stronger walls.
So, engineers need to consider in advance, then decide how they will adapt GRP pipe’s design. For example, smaller length of GRP pipes can solve size issues and transportation, but it can cause installation difficulties instead.
| Disadvantage | Specific Issue | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Brittleness | Cracks from mishandling | Use padded supports, lifting slings, training |
| Repair Challenges | Specialized resin patching needed | Hire trained technicians, budget for costs |
| Temperature Limitations | -40°C to 100°C range | Use heat-resistant resins for high temperatures |
| Environmental Concerns | VOC emissions, recycling difficulty | Explore chemical recycling, assess lifecycle impact |
| Design Constraints | Max 4m diameter, limited thickness | Adjust designs, use multiple pipes |
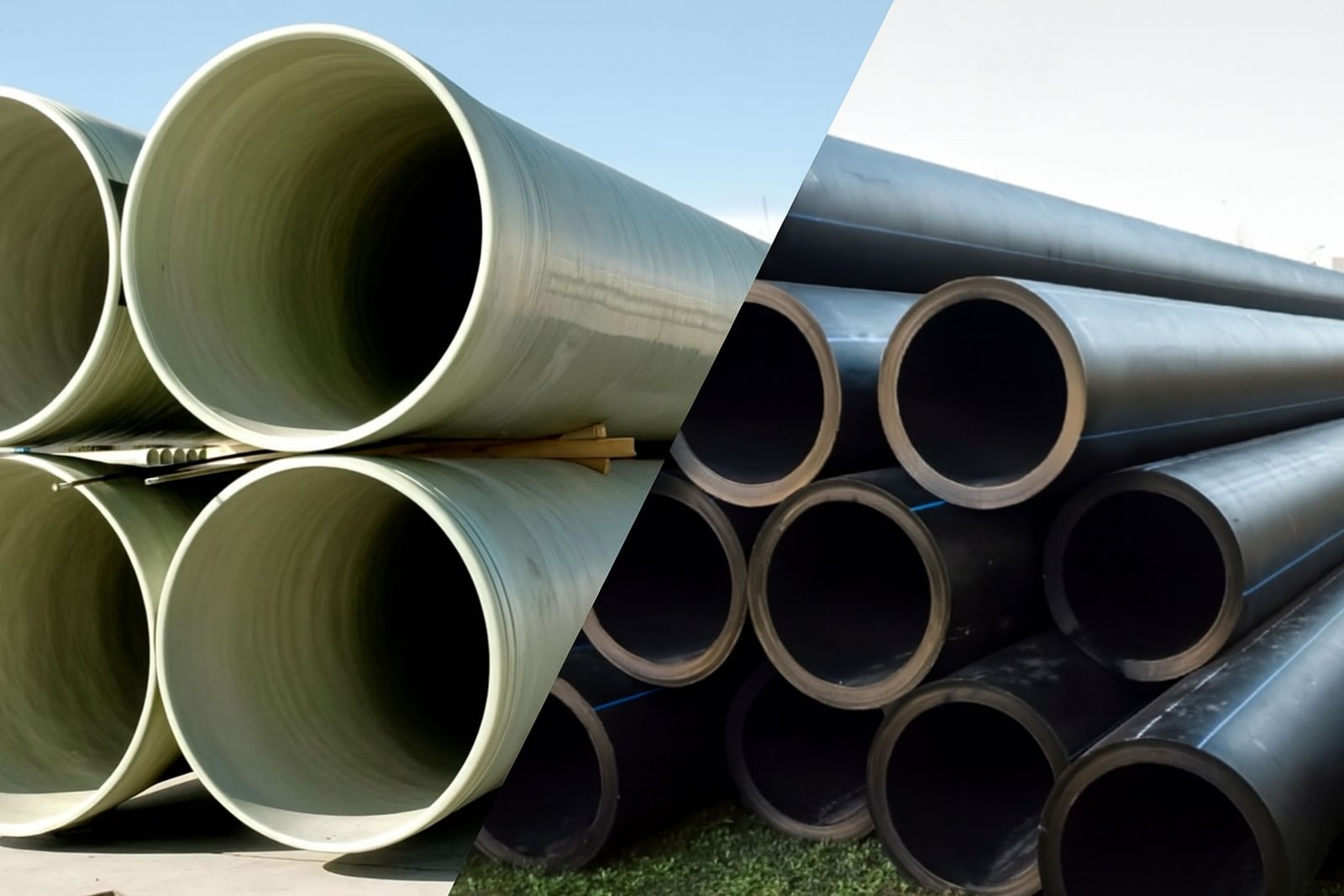
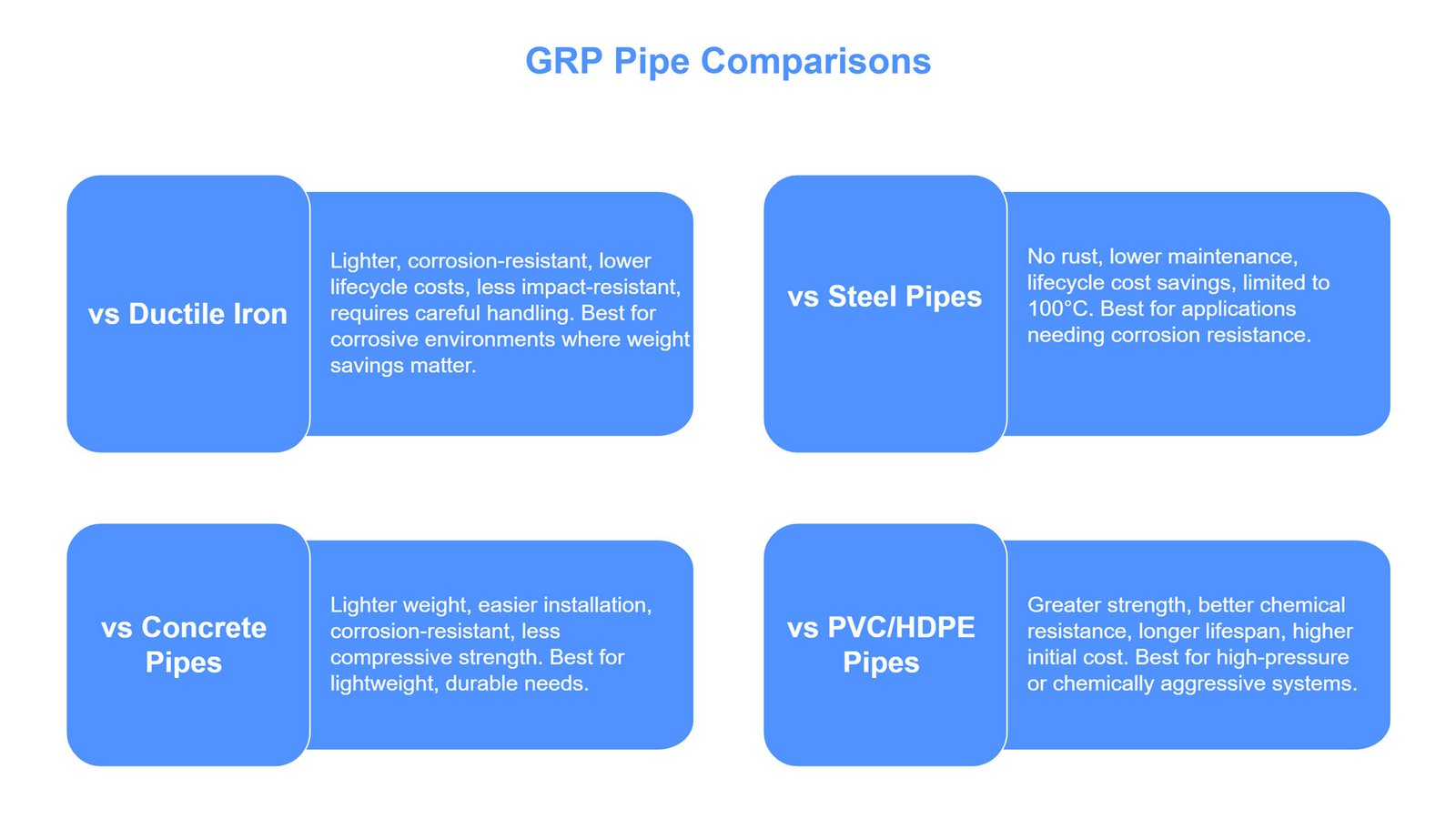
GRP Pipes Compared to Alternative Materials
To aim for the best and long-lasting piping system matched with your project’s demands, choosing the right pipeline matters the most. Above, we evaluate the pros and cons of GRP pipe, let’s figure out how GRP pipe shows itself compared to its alternatives:
- GRP vs Ductile Iron Pipes: GRP pipes include a lighter weight than ductile iron pipe (mostly one-fourth), while corrosion resistance is requested for harsh conditions like wastewater systems, however, GRP pipe needs careful handling.
- GRP vs Steel Pipes: GRP pipes require less maintenance and reduce costs to make a perfect choice for chemical plants, while unlike GRP pipes, steel pipe can handle higher temperatures.
- GRP vs Concrete Pipes: GRP pipe includes 10% of concrete weight and faster installation for water supply lines, but it fails under heavy loads.
- GRP vs PVC and HDPE Pipes: GRP pipe can handle high-pressure systems and provide a longer lifespan, while its higher initial costs should be considered.
Why Choose GrandPipeGroup for Your GRP Pipe Needs?
GrandPipeGroup offers GRP pipes (DN50–DN4000, up to 40 bar), fittings, and full EPCC services for water, wastewater, and industrial projects. International standards such as ISO 9001 and ASTM-certified pipes prove the 50–100+ year lifespans of pipelines in harsh environments.
Our experienced consultants were supporting many projects, whether large-scale or small-scale over years to guarantee a matched pipeline to your demands.
To ensure a long-lasting piping journey, our on-site training and repair technicians are here to secure consistency through custom GRP pipe solutions over time.
Our team in GrandPipeGroup will provide you with lightweight, low-maintenance pipes, delivering 20–40% lifecycle savings, boosting ROI for your projects!
conclusion
GRP pipes advantages and disadvantages provide us with such practical information to select the right piping system for the project. Their corrosion resistance, lightweight nature, and long-lasting lifespan make them perfect for water, sewage and marine systems. However, impact brittleness, repair challenges and manufacturing limitations force engineers to design their pipelines carefully. GrandPipeGroup’ team’s solutions help managers to achieve the best infrastructure meeting their specific demands.
FAQs
1- How long do GRP pipes last?
GRP pipes normally last at least 50 years and interestingly over 100 years under proper condition make GRP pipe perfect for long-term projects like water or wastewater systems and saline conditions.
2- Are GRP pipes recyclable?
Recycling process of GRP pipe is challenging due to its complex combination of glass fibers and resin, but emerging methods like grinding are improving sustainability
3- What’s the temperature limit for GRP pipes?
They handle -40°C to 100°C; special resins extend this for higher temperatures.
4- How do GRP pipes compare to steel?
GRP offers better corrosion resistance and lower costs, but steel handles higher loads in high-pressure systems for those who are seeking easy-to-transport materials, GRP pipes are top choices.
5- Can GRP pipes crack?
Yes, impact brittleness risks cracks if mishandled, requiring careful installation.
about
The Author
Farshid Tavakoli is a seasoned professional in engineering and international trade. Holding degrees in Electrical Engineering, Mechatronics, and a Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA) from the University of Lyon, he also has a strong background in industrial automation and production line technologies.
For over 17 years, he has led an international trading company, gaining deep expertise in commercial solutions tailored to industrial needs. With more than 8 years of active involvement in infrastructure development, he specializes in the supply of electromechanical equipment for water and wastewater treatment plants and transfer projects.
Together with comapny expert team, he now provides consultancy and integrated solutions for sourcing and implementing complex infrastructure projects across the region.




